GI MOTILITY STUDIES
GI Motility Tests
Your gastroenterologist will order a motility test to accurately diagnose your condition and develop an effective treatment plan that addresses your symptoms and manages your disorder.
Esophageal manometry
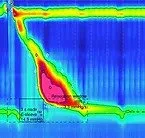
These tests can diagnose several conditions that result in food sticking after it is swallowed. For example, achalasia is a condition in which the muscle of the lower esophageal sphincter does not relax with each swallow to allow food into the stomach. Esophageal manometry is also used to evaluate patients who might have Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Achalasia, Esopahgeal spasms, Dysphagia
Preparation for Motility Tests
Do not eat or drink after midnight the night before the test.
It is best to wear a button-down shirt the day of the test.
Some medications may be stopped before your motility test..
It is best to wear a button-down shirt the day of the test.
Some medications may be stopped before your motility test..
Esophageal Motility Test
An esophageal motility test (esophageal manometry) takes approximately 45 minutes.
Before testing, your technician will verify that you have not eaten anything within six hours of the study. At the start of the test, you will be sitting upright. One nostril will be anesthetized with a numbing lubricant. Your technician will pass a thin, flexible, plastic tube (1/8 inch in diameter) through the numbed nostril, down into the back of your throat and into the esophagus as you swallow. With continued swallowing, the tube is passed into the stomach. With specific instruction the test find will be recorded in program.
